The Science Behind Tints, Films, & Airgas and how it can save you money!

Laminated impact glass combines a robust layer of laminated interlayer between two glass panes, designed to withstand high-impact conditions (e.g., storms and break-ins). When paired with technologies like Low-E coatings and argon gas fills to improve insulation and energy efficiency. Whether you choose clear, tinted, or Low-E impact windows, each option is designed to provide maximum comfort and protection.
TINTS
- Visible Light Transmittance (VLT): Tints like gray or bronze reduce the amount of light that enters your home because they absorb and reflect part of the sunlight. Essentially, the darker the tint, the less light passes through. Tinted windows let in less light, which can make your home darker, but this can be good if you want to reduce glare or heat from the sun. It’s a trade-off between brightness and comfort (less glare, less direct sunlight).
- Lower Cooling Cost: Gray/bronze tints are especially useful in areas with a lot of direct sunlight (like South Florida), where keeping the indoor temperature comfortable can be challenging. They help keep your home more energy-efficient by reducing heat gain during the day, meaning you'll spend less on cooling.
- Privacy: Gray and bronze tints offer more privacy because they make it harder for people outside to see inside your home during the day, especially if the windows face the street or your neighbor’s property. The darker the tint (like gray-gray), the more privacy it provides while still allowing visible light to pass through. This is especially helpful for windows facing a busy street or where you want a little extra seclusion.

LOW-E
Low-E coatings are ultra-thin, invisible layers of metal or metallic oxide applied to the glass surface. These coatings are designed to selectively reflect certain wavelengths of light while allowing others to pass through. Most commonly, Low-E coatings reflect infrared radiation (heat) while transmitting visible light.
- Thermal Insulation (U-Value): Low-E coatings reduce the amount of heat transferred through the glass by reflecting infrared radiation (heat) back into the room. This improves the window’s thermal performance, meaning less heat escapes during the winter and less heat enters during the summer.
- Energy Efficiency: Low-E windows provide superior energy efficiency by combining the benefits of thermal insulation (lower U-value) with solar heat gain reduction (lower SHGC). Low-E coatings reflect infrared radiation and ultraviolet (UV) rays, reducing the amount of solar heat that enters the home. This is particularly beneficial in hot climates like South Florida, where cooling costs can be significant. This consistent temperature also contributes to better overall comfort in the home, making it easier to keep rooms cooler or warmer without relying heavily on HVAC systems.
- UV PROTECTION: Low-E coatings block a significant portion of UV radiation (responsible for fading furniture, flooring, and fabrics) while still allowing natural light to pass through.

Argon Gas
- Thermal Insulation (U-Value): The presence of argon gas in laminated impact glass windows improves their thermal insulation by reducing the rate of heat transfer between the inside and outside of the home. Argon is a dense, non-reactive gas that slows down the movement of heat between the panes of glass, which results in better insulation and a lower U-value.
- Energy Efficiency: With argon gas, laminated impact windows reduce the amount of heat that enters or escapes the home, helping maintain a more stable indoor temperature. This results in lower energy bills for heating and cooling, especially when combined with a Low-E coating, which reflects infrared heat.
- Solar Heat Gain (SHGC): While the addition of argon gas does not directly reduce the SHGC, it enhances the overall thermal performance of the window by preventing the heat gained through solar radiation from escaping back into the home. The effect of argon is more pronounced when combined with Low-E coatings that reflect heat and UV rays.
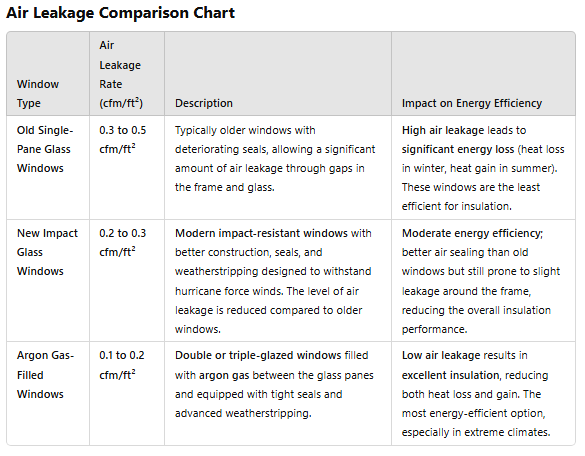
- Air Tightness (Air Leakage): Argon gas also helps to reduce the amount of air leakage through the window, improving overall air sealing and minimizing drafts or heat loss through gaps in the window frame.
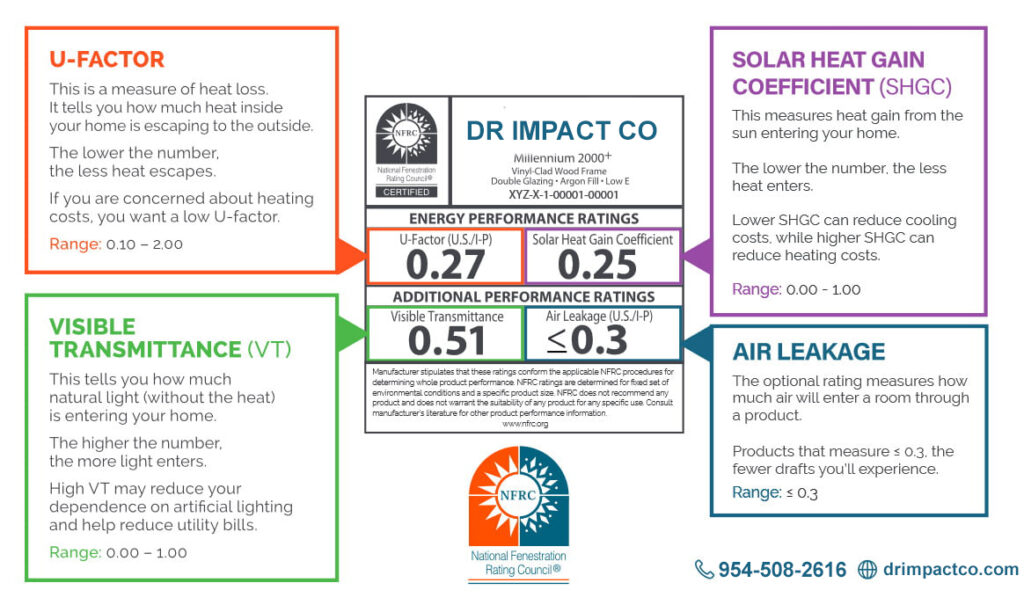
Home Size: 1,300 sq. ft.
Number of Windows: 10 windows (average 15 sq. ft. per window)
Annual Cooling Costs with Old Non-Hurricane Windows: $1,200/year (baseline for single-pane windows)
Energy Cost: $0.12 per kWh
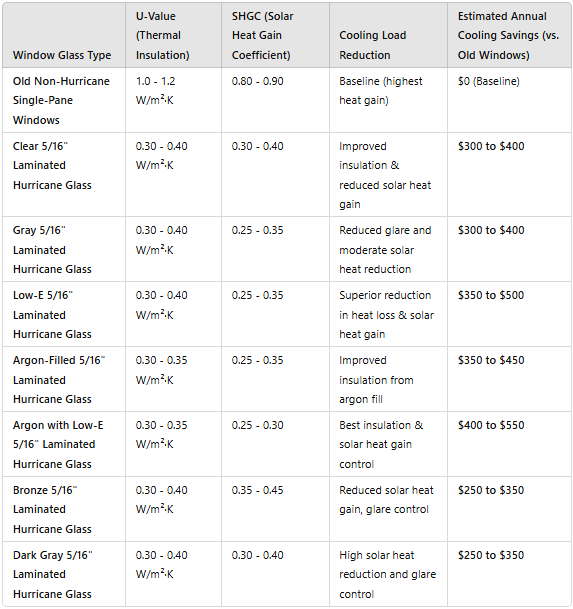
Cooling Energy Savings: Based on improved U-value (thermal insulation), SHGC (solar heat gain coefficient), and thermal performance of laminated hurricane glass in different glazing types.
 |
|
*These savings are AI generated could have different factors on cost per saving by product, usage and quality of the built home *
Clear Laminated Impact Glass (5/16")
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC):
Without Argon Gas: 0.60 – 0.70
With Argon Gas: 0.55 – 0.65
Argon gas typically doesn't affect SHGC significantly but may slightly reduce heat transfer from the sun.
Visible Light Transmittance (VLT):
Without Argon Gas: 75% – 80%
With Argon Gas: 75% – 80%
VLT remains largely the same because it’s a property of the glass, not the gas inside.
U-Value (Thermal Transmittance):
Without Argon Gas: 0.45 – 0.55 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
With Argon Gas: 0.35 – 0.45 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
Argon gas improves the U-value by adding additional insulation between the panes, reducing heat transfer.
Air Leakage (AL):
Without Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.3 cfm/ft²
With Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.2 cfm/ft²
Argon-filled windows can have slightly better air sealing and reduce air leakage.
Gray Laminated Impact Glass (5/16")
SHGC:
Without Argon Gas: 0.50 – 0.60
With Argon Gas: 0.45 – 0.55
Gray tint helps reduce solar heat gain compared to clear glass, and adding argon can slightly enhance the insulating properties.
VLT:
Without Argon Gas: 40% – 45%
With Argon Gas: 40% – 45%
The tint remains the same with or without argon gas.
U-Value:
Without Argon Gas: 0.50 – 0.60 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
With Argon Gas: 0.40 – 0.50 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
Argon gas improves the U-value and enhances energy efficiency.
Air Leakage:
Without Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.3 cfm/ft²
With Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.2 cfm/ft²
Argon-filled windows tend to have slightly improved air sealing.
Bronze Laminated Impact Glass (5/16")
SHGC:
Without Argon Gas: 0.45 – 0.55
With Argon Gas: 0.40 – 0.50
The addition of argon gas will improve the thermal performance slightly, reducing the amount of heat entering the home.
VLT:
Without Argon Gas: 35% – 40%
With Argon Gas: 35% – 40%
Bronze tint does not change with the addition of argon gas.
U-Value:
Without Argon Gas: 0.50 – 0.60 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
With Argon Gas: 0.40 – 0.50 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
The addition of argon gas helps to further reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency.
Air Leakage:
Without Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.3 cfm/ft²
With Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.2 cfm/ft²
Argon helps to slightly improve air sealing by reducing air leakage.
Gray-Gray Laminated Impact Glass (5/16")
SHGC:
Without Argon Gas: 0.40 – 0.50
With Argon Gas: 0.35 – 0.45
Gray-gray laminated glass reduces solar heat gain even further, and argon gas improves insulation slightly.
VLT:
Without Argon Gas: 30% – 35%
With Argon Gas: 30% – 35%
The VLT remains unaffected by the presence of argon gas.
U-Value:
Without Argon Gas: 0.50 – 0.60 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
With Argon Gas: 0.40 – 0.50 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
Argon gas offers a noticeable improvement in thermal efficiency by reducing heat loss.
Air Leakage:
Without Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.3 cfm/ft²
With Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.2 cfm/ft²
Argon improves the overall air tightness of the window.
Low-E Laminated Impact Glass (5/16")
SHGC:
Without Argon Gas: 0.20 – 0.30
With Argon Gas: 0.18 – 0.28
Low-E glass with argon improves thermal performance by reducing solar heat gain even further.
VLT:
Without Argon Gas: 60% – 70%
With Argon Gas: 60% – 70%
The VLT remains the same since the Low-E coating is the primary factor for light transmission, not the gas.
U-Value:
Without Argon Gas: 0.30 – 0.35 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
With Argon Gas: 0.25 – 0.30 BTU/hr·ft²·°F
Argon gas significantly reduces the U-value of Low-E laminated impact glass, making it one of the most energy-efficient options available.
Air Leakage:
Without Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.3 cfm/ft²
With Argon Gas: 0.1 – 0.2 cfm/ft²
Argon gas contributes to slightly improved air sealing, which is an important factor in reducing energy loss.
How Argon Gas Improves Performance:
- Thermal Insulation (U-Value): The presence of argon gas in laminated impact glass windows improves their thermal insulation by reducing the rate of heat transfer between the inside and outside of the home. Argon is a dense, non-reactive gas that slows down the movement of heat between the panes of glass, which results in better insulation and a lower U-value.
- Energy Efficiency: With argon gas, laminated impact windows reduce the amount of heat that enters or escapes the home, helping maintain a more stable indoor temperature. This results in lower energy bills for heating and cooling, especially when combined with a Low-E coating, which reflects infrared heat.
- Solar Heat Gain (SHGC): While the addition of argon gas does not directly reduce the SHGC, it enhances the overall thermal performance of the window by preventing the heat gained through solar radiation from escaping back into the home. The effect of argon is more pronounced when combined with Low-E coatings that reflect heat and UV rays.
- Air Tightness (Air Leakage): Argon gas also helps to reduce the amount of air leakage through the window, improving overall air sealing and minimizing drafts or heat loss through gaps in the window frame.
Conclusion:
Adding argon gas to 5/16" laminated impact glass significantly improves the thermal insulation and overall energy efficiency of the window. The most noticeable improvement is in the U-value, which is the measure of heat transfer. Windows with argon gas are more effective at maintaining a comfortable temperature in your home, reducing your reliance on heating and cooling systems, and ultimately lowering energy costs.
Low-E laminated impact glass with argon offers the best performance in terms of energy savings, reducing both heat gain and loss, while maintaining natural light levels.